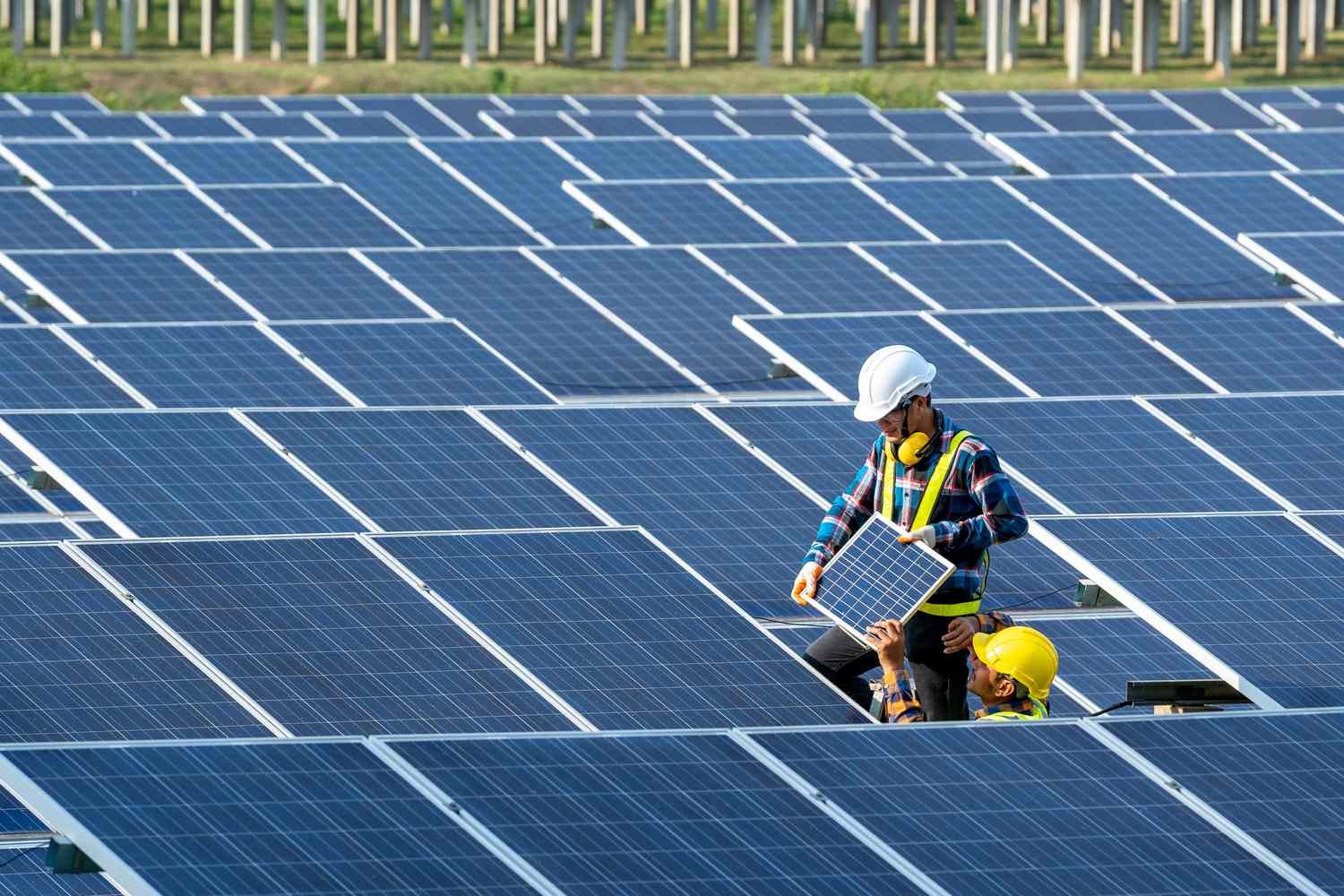
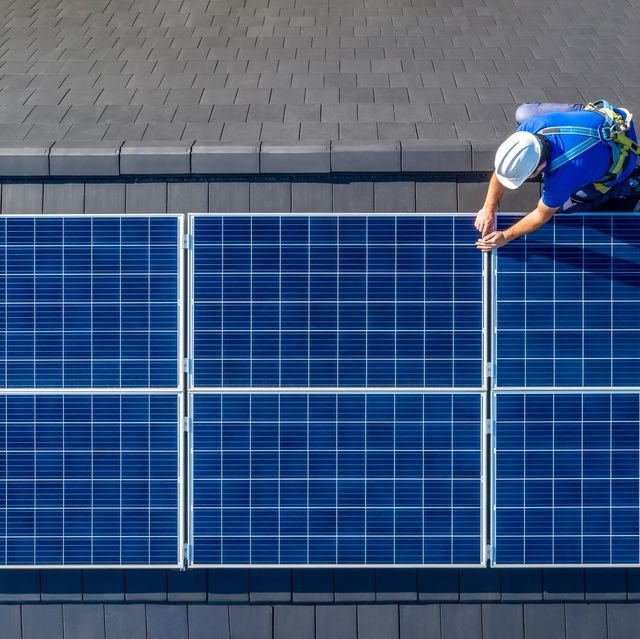
In the face of climate change and rising energy costs, solar module installation has emerged as a powerful, long-term solution. It is not just about reducing electricity bills—it’s about empowering homes and industries to be energy independent, eco-conscious, and future-ready. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to reduce your carbon footprint or a manufacturing plant seeking to cut down operational expenses, installing solar modules is a game-changing decision.
Table of Contents
What is Solar Module Installation?
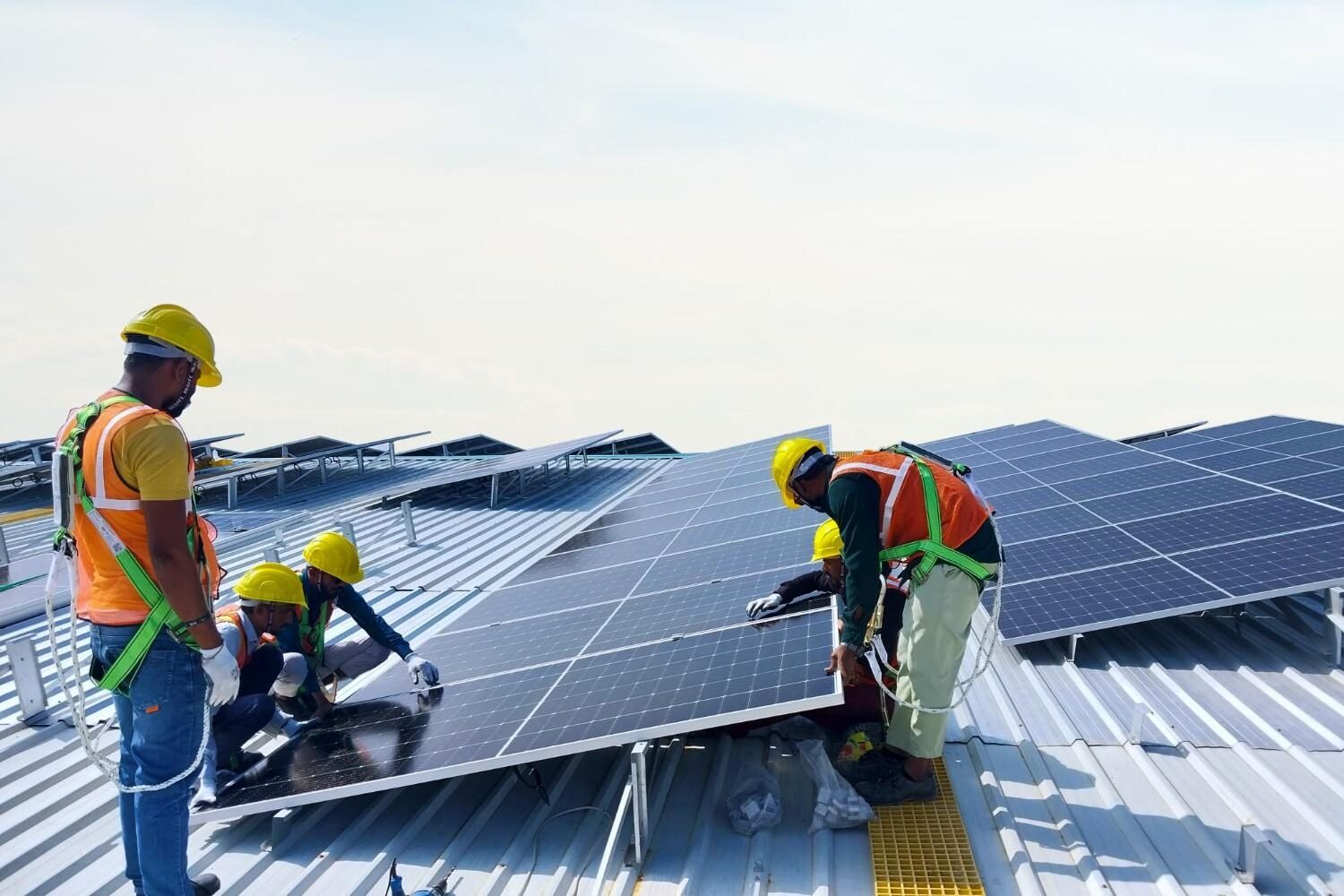
Solar module installation is the process of installing solar panels on surfaces like rooftops, ground structures, or carports to convert sunlight into electricity. It involves the physical and electrical integration of the solar energy system, transforming passive sunlight into active energy savings. This process involves mounting photovoltaic (PV) panels on structures and integrating them into a functional solar power system to generate clean electricity.
Solar module installation is essential for enabling solar panels to transform sunshine into usable electricity. This system reduces energy bills, supports sustainability goals, and empowers businesses and homes to generate renewable energy independently.
Types of Solar Module Installations
1. Monocrystalline PV Modules
- Made from single-crystal silicon wafers—uniformly black in appearance.
- Highest commercial efficiency (≈ 15–22%) → ideal when space is limited.
- More costly but offers better long-term performance.
2. Polycrystalline PV Modules
- Constructed from multiple silicon crystals; typically blue-speckled.
- Efficiency around ~15%, lower cost than monocrystalline.
- Requires more area for comparable energy output.
3. Thin-Film Modules
- Flexible and lightweight; uses materials like CdTe, CIGS, or amorphous silicon.
- Efficiency ranges roughly 10–12%; often used in large-scale utility setups.
- Cost-effective for large areas and adaptable design.
4. Bifacial Modules
- Can generate power from both front and rear surfaces.
- When combined with tracking systems, can boost annual output by 10–30%.
5. Hybrid Photovoltaic-Thermal (PVT) Modules
- Produce electricity while capturing heat from the same panel.
- Enhanced overall efficiency; heat may be used for domestic water or HVAC.
6. Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
- Modules integrated into building materials.
- Examples include solar shingles and semi-transparent wall panels.
- Offers aesthetics and dual functionality (structure + energy).
Step-by-Step Process of Solar Module Installation
Site Assessment and Feasibility Study
Professionals conduct site surveys to assess roof or ground conditions, including roof orientation, structural strength, shading issues, and available space. They also evaluate energy usage and solar system types. Engineers evaluate the location to understand space, sunlight availability, shading, roof angle, and structure. The process starts with an estimate of energy required and property measurement. The roof should be sound, have a lifespan of 15-20 years, and catch direct sunlight. The orientation and tilt of the roof, and shading analysis, should also be considered.
System Design and Engineering
Engineers create a custom solar layout based on energy needs, roof area, panel orientation, and preferred inverter type. Permits and incentive applications are arranged. After site analysis, a solar system is designed based on daily electricity usage, system size, and type of inverter. The layout is tailored to your energy needs, available space, and budget, ensuring an efficient and cost-effective solution.
Procuring Equipment
The solar system comprises monocrystalline, polycrystalline, bifacial, or smart modules, an inverter for DC to AC power conversion, mounting structures, UV/temperature-resistant cabling, and MC4 connectors, all sourced from reputable sources.
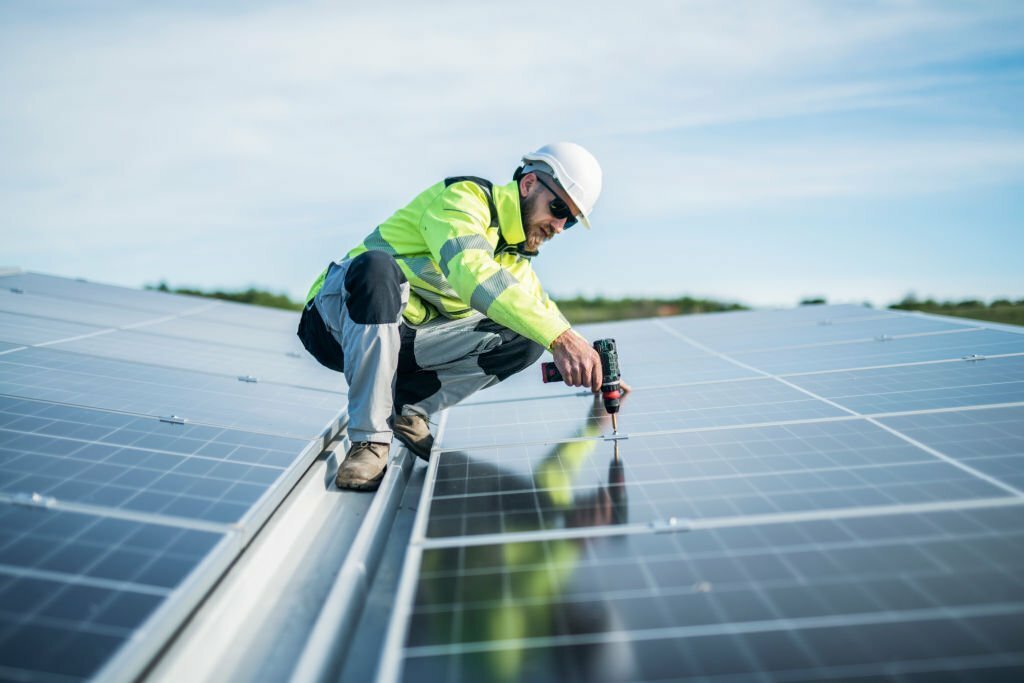
Mounting Structure Installation
Solar panels are installed on a solar array using a secure mounting system. The frame is anchored to withstand wind, rain, and temperature changes, and the panels are bolted with precise spacing for optimal sun exposure. The tilt angle is set at the location’s latitude for maximum annual yield. The mounting structure is prepared for stability and durability, with roof-mounted systems using brackets and ground-mounted options using sturdy frames. The structure is then installed according to manufacturer’s specifications, with proper alignment for optimal energy capture. The system provides a solid foundation for the solar cells, ensuring their longevity and performance.
Electrical Wiring and Connection
Solar panels are wired in series or parallel based on voltage and current requirements, using MC4 connectors and weather-resistant conduit. Wiring must follow local electrical standards and include earthing and surge protection. All DC lines feed into the inverter, which connects to the AC electrical panel or energy storage system. Correct wiring is crucial for the system’s functionality, with series connections increasing voltage and parallel setups enhancing amperage. Insulation is essential to avoid short circuits and hazards, and using electrical conduit shields wiring promotes safety and extends installation lifespan. Well-organized wiring facilitates aesthetics and future maintenance.
Testing and Commissioning
Initial testing verifies connections, insulation resistance, and grounding, while performance testing measures voltage, current, and efficiency of panels and inverters. Comprehensive documentation is compiled, and final inspections by local authorities and utilities enable grid interconnection or net-metering permissions. Testing is crucial for commissioning, including PV modules, earthing, inverters, and wiring. Insulation resistance is one of the first tests, ensuring no leakage current. As the plant is expected to last 25 years, recording resistance values and tracking them over the plant’s life can provide valuable information on insulation deterioration and quality.

Cost of Solar Module Installation
Residential Solar Installation Costs
System Size & Price Range (Before Subsidy)
- 1 kW: ₹45,000 – ₹75,000
- 3 kW: ₹1.9 – 2.4 lakh
- 5 kW: ₹3.15 – 3.57 lakh
- 7–10 kW: ₹4.0 – 4.6 lakh
Subsidy Scheme: PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana
- ₹30,000 per kW for first 2 kW
- ₹18,000 for 3rd kW
- Total max subsidy = ₹78,000
Subsidy Scheme: PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana
- 1 kW: ₹15,000 – ₹45,000
- 3 kW: ₹1.12 – 1.62 lakh
- 5 kW: ₹2.37 – 2.79 lakh
Commercial & Industrial Installations
- Typical cost ranges from ₹35,000 – ₹50,000 per kW, depending on scale, complexity, and panel type
- Installation costs include mounting, wiring, inverter, PDU, labor, and approvals per kW at ₹10–15/W
Decision-makers often see shorter ROI with larger systems due to economy of scale, tax benefits (accelerated depreciation, GST credits), and minimal maintenance requirements
Benefits of Solar Module Installation
1. Substantial Cost Savings & ROI
- Slash your electricity bills — Systems can offset 70–90% of your energy usage, depending on size and usage patterns.
- Fast payback — Many residential and commercial setups pay for themselves within 3–5 years, with decades of free energy ahead.
- Net metering allows you to sell surplus energy back to the grid, turning unused capacity into utility credits or revenue.
2. Environmental Impact & Sustainability
- Clean & renewable energy — Solar power emits zero greenhouse gases during generation, reducing carbon footprints and air pollution.
- Supports India’s green goals — Huge deployments across Gujarat and other states are already avoiding thousands of tons of CO₂ emissions.
- Reduced fossil fuel dependency strengthens national energy security and resilience.
3. Energy Independence & Grid Security
- Self-generation empowers manufacturers — Decisions-makers control energy flows, reducing vulnerability to grid instability and escalating tariffs.
- Battery backup or hybrid systems can maintain operations during blackouts, ensuring uninterrupted power for critical C&I workloads.
4. Low Maintenance & High Reliability
- Minimal upkeep — With no moving parts, systems typically need only periodic cleaning and annual checks to sustain peak performance.
- Durability guaranteed — Most solar modules come with 25-year performance warranties and often operate efficiently well beyond 30 years.
5. Boosted Asset Value & Brand Image
- Property resale value increases — Solar-equipped properties command a premium (around 3–4% more) in valuations.
- Strengthen corporate reputation — Installing solar improves Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), resonates with eco-conscious customers, investors, and employees.
6. Government Incentives & Economic Benefits
- Subsidies make systems accessible — Example: indicates up to ₹78,000 subsidy for residential systems under PM Surya Ghar Yojana.
- Tax advantages for C&I — Accelerated depreciation (40%), GST input credits, and state-specific rebates maximize returns.
- Broad promotion of rooftop solar — Large-scale government programs (e.g. PM Surya Ghar) are streamlining approval and subsidy flows at scale.
7. Economic Growth & Job Creation
- Local employment — Every solar installation fuels jobs across EPC, logistics, maintenance, and manufacturing, driving local economic uplift.
- Stimulates green sector innovation — Expanding solar systems supports the ecosystem of advanced technology and skilled labor.
8. Operational Advantages & Scalability
- Flexible system design — From rooftops to carports, and agrivoltaics, solar can adapt to varied industrial architectures.
- Scalable over time — Manufacturers can pilot a smaller system and gradually expand capacity as the business grows

Challenges in Solar Module Installation and Their Solutions
1. Structural & Safety Risks
- Problem: Substandard mounting structures may collapse during storms—panels have flown off rooftops in 120 km/h winds in places like Indore and Bhopal. These systems fail within a few years due to rust and poor design.
- Solution: Use engineered, pre‑fabricated mounting systems (like those certified to IIT standards) capable of withstanding wind speeds up to 170 km/h, along with professional structural engineering assessments.
2. Quality & Durability Concerns
- Problem: Many panels degrade prematurely—warranty periods end after just 8–12 years due to micro-cracks, poor soldering, and unsuited build materials for India’s climate.
- Solution: Prioritize Tier-1 modules with long-term performance warranties and quality certifications. Implement routine monitoring and quality audits post-installation.
3. Dust, Soiling & Water Scarcity
- Problem: Dust accumulation in regions like Rajasthan and Gujarat lowers module efficiency by up to 30%. Combined with water hardness, cleaning becomes costly and difficult.
- Solution: Schedule regular cleaning (especially in dusty zones), use water treated via RO systems, consider automated or hydrophobic coatings, and employ dry-cleaning technologies where viable.
4. Shading & Site-Specific Design Issues
- Problem: Shadows from trees, HVAC, or surrounding obstructions can significantly reduce yield and cause hot spots.
- Solution: Conduct detailed shading analysis during planning. Deploy micro-inverters or optimizers to mitigate output loss and adjust layouts to avoid shading zones.
5. Grid Integration & Electrical Constraints
- Problem: Reverse power flow, intermittent PV output, and voltage variability can destabilize distribution systems that weren’t designed for bi-directional power flow.
- Solution: Implement smart grid tech, energy storage solutions (like lithium-ion batteries), and O&M remote monitoring to smooth generation ramps and balance feed-in across the grid.
6. Regulatory, Permitting & Policy Barriers
- Problem: Complex approvals, inconsistent state-by-state net-metering rules, and coordination delays with DISCOMs slow rollout and frustrate consumers.
- Solution: Work with EPC partners that provide single-window assistance, standardize net-metering application with utilities, and ensure accurate digital submission for subsidy eligibility.
7. Financial & Market Challenges
- Problem: High up-front costs, uncertain subsidy disbursals, import duties on components, and fluctuating availability impact feasibility.
- Solution: Leverage government loans, solar financing programs, green bonds, and local manufacturing schemes under “Make in India” to reduce reliance on imports and secure financing stability.
8. Skilled Workforce Shortage
- Problem: Limited availability of qualified designers and certified installation teams leads to errors, delays, and compromised quality.
- Solution: Invest in vocational training, certifications, and partnerships with technical institutes. EPC companies should standardize and standard-operating-procedure their workforce operations.
9. Health & Occupational Safety Concerns
- Problem: Workers face risk of falls, electrocution, ergonomic strain, and exposure to toxic materials during installation or handling waste panels.
- Solution: Enforce strict safety protocols: harness use, electrical isolation, PPE, worker training, and safe e-waste disposal practices.
10. End-of-Life and Waste Management
- Problem: With solar panel installations expected to reach 50–325k tonnes of waste by 2030, informal recycling and improper disposal pose environmental risks.
- Solution: Implement recycling programs under E-waste regulations, support producer responsibility legislation, and develop infrastructure for safe PV module disposal.

Government Incentives for Solar Module Installation
PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana (Flagship Residential Rooftop Solar Scheme)
- Launch & Mandate
Approved on February 29, 2024, this ₹75,021 crore MNRE-backed initiative targets 1 crore residential rooftops by March 2027, offering free electricity up to 300 units/month. - **Subsidy Structure (Central Financial Assistance / CFA)**
‣ Up to 2 kW: 60% subsidy (~₹30,000/kW)
‣ 2 – 3 kW: 40% of additional cost (cap at ₹78,000 for > 3 kW)
‣ Max subsidy: ₹78,000 for systems ≥ 3 kW. - Eligibility & Application
Open to Indian citizens with valid electricity connections and suitable rooftops. Must not have received previous solar subsidies. Apply through the MNRE portal —includes feasibility approvals, vendor selection, net-metering, and inspection workflows. Subsidy is credited to the bank account within ~30 days post-installation. - Additional Benefits
‣ Collateral-free loans up to ₹2 lakh at ~7% interest available.
‣ One Model Solar Village created per district to showcase implementation.
‣ Scheme expected to generate ~17 lakh direct jobs and add ~30 GW of rooftop solar capacity.
Best Practices for Successful Solar Module Installation
1. Thorough Site Assessment and Feasibility Study: Before installation, analyze roof space, orientation, shading, structural analysis, and solar irradiance mapping to ensure long-term physical and financial viability of the system.
2. Optimal System Design: Utilize high-efficiency solar modules suitable for your climate zone, select an inverter that matches capacity and voltage needs, and design for minimal transmission losses and maximum energy yield.
3. Quality Equipment and Materials: Select Tier 1 solar modules, premium mounting structures, and reliable balance-of-system components for improved performance and a 25+ year system life.
4. Skilled EPC Partner: Partner with a professional Solar EPC company like Soleos Solar for proven C&I experience, on-time delivery, and certified engineers to avoid costly rework, compliance issues, and operational downtime.
5. Adherence to Safety and Compliance Standards:The guidelines include BIS and MNRE guidelines, international standards like IEC and ISO, local DISCOM and fire safety codes, emphasizing safety first by integrating grounding, surge protection, and fire-resistant cabling.
6. Efficient Installation Planning: Schedule for low-rain seasons, coordinate civil, electrical, and logistics teams, and use appropriate tools for alignment, torque, and angle calibration.
7. Monitoring System Integration: Smart solar monitoring systems, whether cloud-based or on-premises, can track generation, identify faults quickly, and enable predictive maintenance, with mobile app access and remote diagnostics recommended.
8. Post-Installation Testing and Commissioning: Perform IV curve, insulation resistance, and thermal imaging tests, verify inverter synchronization and grid connectivity, and ensure full load testing before handover.
9. Operations & Maintenance (O&M) Plan: Implement a preventive maintenance schedule, including panel cleaning, electrical checks, and visual inspections, and outsource O&M to a reliable provider for warranty compliance and uninterrupted performance.
10. Documentation and Warranty Management: The document includes equipment datasheets, warranty certificates, single-line diagrams, layout drawings, and maintenance logs, ensuring transparency and supporting future audits, resale, or scale-up.

Future Trends in Solar Module Installation
The future of solar module installation is experiencing a revolutionary transformation fueled by advancements in technology, automation, and a global shift toward sustainability. Innovations such as bifacial solar modules—which generate power from both sides—are significantly enhancing energy yields, making solar module installation more efficient and productive than ever. At the same time, cutting-edge perovskite-silicon tandem cells are pushing efficiency levels beyond 30%, redefining the standards for high-performance solar module installation across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Aesthetic integration is also becoming a key focus, with Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) making solar module installation more seamless and visually appealing in modern architecture. Additionally, smart technologies like AI-powered monitoring and predictive maintenance are now essential components of intelligent solar module installation, ensuring reliability, early fault detection, and minimal downtime. Automation is also playing a major role in the future of solar module installation, with robotic systems and drones drastically reducing labor time, increasing safety, and enabling faster project completion on large-scale solar farms.
Emerging practices such as agrivoltaics are redefining land use by combining agriculture with solar module installation, while floating solar systems are utilizing water surfaces to boost efficiency and conserve space. The integration of advanced battery storage solutions with solar module installation is enabling around-the-clock power supply, offering greater energy security and autonomy for manufacturing and industrial units. Moreover, enhanced safety protocols—like arc fault detection and rapid shutdown systems—are now a core part of commercial solar module installation strategies, ensuring compliance and protection.
Finally, with trends like peer-to-peer energy trading and decentralized power generation gaining traction, solar module installation is becoming more accessible, scalable, and financially rewarding. Altogether, these innovations mark a new era in solar module installation, empowering businesses and communities to embrace a smarter, more resilient, and sustainable energy future.
Why Choose Soleos Solar for Your Solar Module Installation?
When it comes to solar module installation, Soleos Solar stands out as a trusted industry leader with over 12 years of global expertise and a portfolio exceeding 450MW+ of successful projects. We specialize in end-to-end EPC solutions for commercial, industrial, and utility-scale solar systems—tailored to maximize performance, efficiency, and long-term ROI. At Soleos Solar, we don’t just install panels—we engineer energy independence. From advanced site assessment and precision design to world-class components and smart monitoring systems, our approach to solar module installation ensures quality, compliance, and sustainability at every step.
Whether you require a rooftop, ground-mounted, agrivoltaic, or solar carport system, our team delivers customized solutions with minimal disruption and maximum reliability. With a strong presence in India, the UK, UAE, Germany, Kenya, Spain, and Portugal, Soleos Solar brings international standards to every local installation. Choose Soleos Solar for your solar module installation—where innovation meets execution, and your transition to clean energy becomes smooth, secure, and scalable.
Conclusion
As global energy dynamics shift, solar module installation is redefining how industries approach sustainability and savings. With innovations like bifacial panels, real-time performance monitoring, and AI-powered energy optimization, solar technology is not only reliable—it’s revolutionary. Businesses that invest in solar today gain more than energy efficiency; they earn a competitive edge and environmental leadership. At Soleos Solar, we combine global expertise with localized support to deliver future-ready solar module installation for commercial and industrial leaders. Our solutions are designed to reduce your carbon footprint, cut electricity costs, and ensure seamless scalability.
Ready to embrace solar for your business? Contact Soleos Solar today to schedule a consultation and power your future with clean, intelligent energy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is solar module installation?
Solar module installation refers to the process of setting up photovoltaic (PV) panels to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. This includes site assessment, system design, mounting structure installation, electrical connections, and system testing.
2. How long does it take to install solar modules?
The time required varies depending on the project size. For most commercial and industrial setups, solar module installation can take anywhere from 1 week to 4 weeks, including site preparation and commissioning.
3. What is the average lifespan of solar modules?
Most high-quality solar modules come with a performance warranty of 25 years, but they can last up to 30 years or more with proper maintenance.
4. How much space is needed for solar module installation?
Space requirements depend on your energy goals. For industrial rooftops or ground-mount systems, expect to need 100–120 sq. ft. per kW of solar installation.
5. What are the key benefits of installing solar modules?
- Lower electricity bills
- Government subsidies & tax benefits
- Low maintenance
- Sustainable and eco-friendly power
- Increased property value