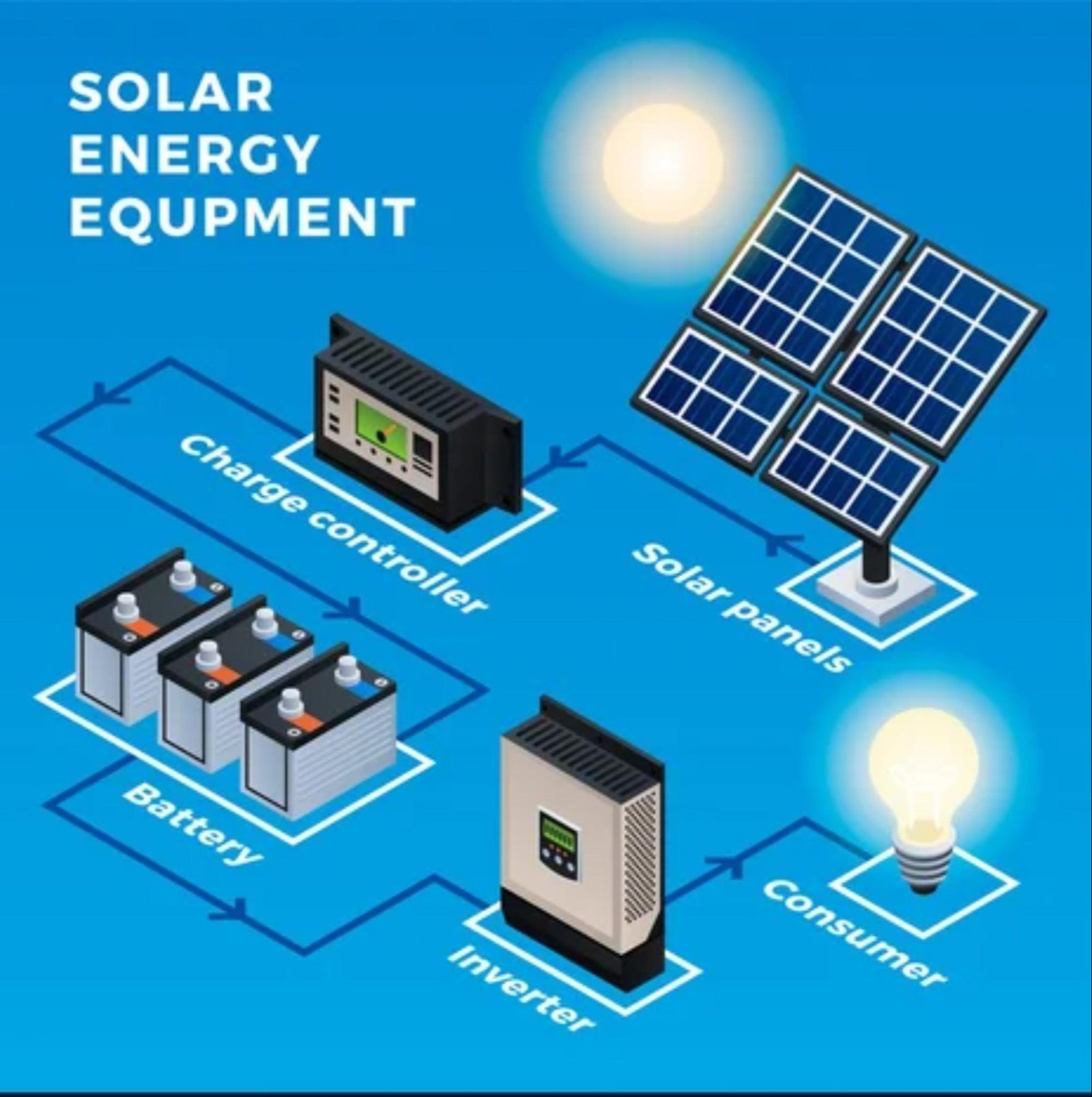
As the world shifts toward renewable energy, solar energy equipment plays a critical role in harnessing the power of the sun. From photovoltaic (PV) panels to inverters and batteries, these components form the backbone of any solar power system. This blog explores the various types of solar energy equipment, their functions, and how they contribute to creating efficient and sustainable solar power systems.
Table of Contents
Understanding Solar Energy Equipment
The parts that make up a solar energy system are called solar energy equipment. The installation of the equipment makes it possible to capture solar energy and transform it into the electricity required for the particular residence or place of business. Several essential parts, including solar panels, inverters, and racking systems, are also included in the solar equipment.
Photovoltaic (PV) Panels
The components of a photovoltaic (PV) system include one or more solar panels, an inverter, and additional mechanical and electrical components that harness solar energy equipment to produce electricity. PV systems come in various sizes, from little rooftop or portable systems to enormous utility-scale generating plants. This article focuses on grid-tied PV systems, which are systems that are connected to the utility grid, even if off-grid PV systems can function independently.
A process known as the photovoltaic effect occurs when photons, which are energy packets, fall from the Sun onto a solar panel and produce an electric current. Although each panel generates a very tiny quantity of electricity, they can be connected to form a solar array to generate larger amounts of energy. A solar panel (or array) generates power in the form of direct current (DC). Even though your phone and laptop are among the numerous electronic gadgets that use DC electricity, they are made to run on the electrical utility system, which supplies (and needs) alternating current (AC). Therefore, an inverter must be used to convert the solar electricity from DC to AC before it can be used.
Key Features
- Made from materials like monocrystalline or polycrystalline silicon.
- Available in various sizes and efficiency levels.
- Durable with lifespans exceeding 20 years.

Solar Inverters
One of the most crucial components of a solar energy system is an inverter. It is a device that transforms solar-generated direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used by the electrical grid.
Types
1. String Inverters
A string of solar panels, or a “string,” is connected to a single inverter via string inverters. The combined DC power from these panels is subsequently transformed into AC power by the inverter. Because of their affordability and ease of use, string inverters are widely used. They might not be the best option for roofs with shading problems, though, because if one panel is shaded, the output of the entire string may decrease.
2. Microinverters
Micro-inverters are another type of solar inverter. Micro-inverters, as opposed to string inverters, are affixed to every solar panel. Each panel may individually convert DC to AC with this configuration. Efficiency is increased with micro-inverters, particularly when individual panels are exposed to varying amounts of sunshine or shade. They also make it simpler to keep an eye on the performance of each panel.
3. Hybrid Inverters
One adaptable option is provided by hybrid solar inverters. They can be connected to a battery storage system in addition to converting DC to AC. With the help of this function, you can store extra solar energy equipmentfor use at other times. Hybrid inverters may provide a dependable power supply and maximize your solar investment, making them an excellent alternative for people wishing to strengthen their energy independence.
Mounting Structures
Mounting structures secure solar panels in place and ensure optimal sunlight exposure.
Types
1. Rooftop Mounting Structure
On the concrete roof of a building, a rooftop mounting structure, also known as a reinforced cement concrete (RCC) mounting structure, is erected. In both residential and commercial solar installations, it is the ideal structure for solar panels. A home, company, school, college, institution, etc. can all have rooftop solar systems installed. The distance between the solar panel and the solar inverter is reduced with the RCC mounting arrangement. Consequently, the likelihood of DC losses in this mounting configuration is reduced. To continue using the area beneath the construction, you can raise it. You can raise the height of the mounting framework to continue using the area beneath the solar panels. It will clear the area beneath.

Advantages of Rooftop Mounting Structure
- You can maintain and clean solar panels easily.
- Its installation cost is low, coming at around Rs. 8/kW.
- Generation of free electricity from unutilised rooftop space.
Disadvantages of Rooftop Mounting Structure
- Drilling on the rooftop may impact the rooftop health.
- Must ensure that the rooftop space is free from shadows.
- Correct solar panel orientation is necessary on your free rooftop space.
2. Ground Mounting Structure
If you have less space or a less shaded area of your roof, you can install a ground mounting structure rather than a rooftop mounting structure. This structure is mounted on the ground using metal frames, as the name implies. This kind of mounting structure is likely to draw dirt because it is buried in the ground. Your ground-mounted solar panels require routine cleaning.

Advantages of Ground Mounting Structure
- Adjustable brackets in the ground mounting structure let you orient the solar panels effectively as per the specific season in your location for maximum exposure to the sun.
- Inspection, maintenance and cleaning of the solar panels become easier in the ground mounting structure.
- You can easily add more solar capacity if there is enough space available on the ground.
Disadvantages of Ground Mounting Structure
- Getting shade-free ground for installing this ground mounted solar panel structure is one of the biggest challenges. As they are closer to the ground, it is more subject to getting shade from nearby trees or buildings.
- It is difficult to install ground mounted solar panel structures in densely populated areas.
- You may have to adjust to the aesthetic of this mounting structure, especially if you are installing this solar system for your home.
3. Floating Mounting Structure
A floating mounting structure floats on a body of water, as the name implies. High-density polyethene (HDPE) is used to create a floating mounting system for solar modules. Lakes, rivers, ponds, reservoirs, and other bodies of water with still water can all have it installed. To keep the building afloat, it is fastened to dead weights. When there is an abundance of open space on a body of water and a lack of free space on land, a floating structure may be a smart option.
The efficiency of a system is also increased by the cooling impact of water. Ramagundam, Telangana, is home to India’s biggest floating mounting structure. It has 4.5 lakh “Made in India” solar PV modules and has a 100 MW capacity.

Advantages of Floating Mounting Structure
- Capitalisation of large waterland like dams, lakes and reservoirs in productive way.
- Conservation of water by decreasing the evaporation rate.
- It can help avoid site preparation and land acquisition costs.
Disadvantages of Floating Mounting Structure
- Floating mounting structure is commercially viable for mostly large scale solar projects, not for residential purposes.
- It is suitable only for specific locations with standstill waterbodies.
4. Pole Mounted Structure
You can erect a pole on a concrete slab for installing your solar system. You may be unable to install a mounting structure on your roof due to insufficient space. A pole-mounted structure is a viable alternative to a rooftop solar structure. Such structures are usually installed on private properties, commercial establishments, and agricultural land. A tracking system can maximise the efficiency of the solar energy equipment.

Advantages of Pole Mounted Structure
- You can install pole mounted solar structures despite limited ground space availability.
- This type of solar mounting structure can avoid the shading effect coming from nearby trees and other vegetation and increase sun exposure.
- As the panels stay higher from the ground, it has less chance of being impacted by human-made vandalism.
Disadvantages of Pole Mounted Structure
- Pole mounted structure is suitable for solar panel systems with less capacity.
- It stands on a single pole, and as a result, it has the risk of falling down during a heavy storm.
5. Carport Solar Module Mounting Structure
A parking lot can have a solar system installed on top of it. Sports stadiums, airports, shopping centers, and other locations can all have a carport mounting structure erected. The mounting framework for a carport is situated on the roof of a carport or vehicle shed. In order to give cars enough room, it remains at a specific height. A DISCOM’s grid receives solar power from an on-grid solar system installed with a carport mounting structure. It may be able to completely eliminate an establishment’s electrical costs. To find out more about on-grid solar systems, check out our blog.

Advantages of Carport Mounting Structure
- Lets you utilise the space beneath the solar panel as shedding.
- Protects your vehicles from potential damage caused due to rain, heat, hailstorm, snowfall or other harsh weather conditions.
- Can integrate solar EV charging facility.
Disadvantages of Carport Mounting Structure
- The upfront installation cost of carport mounting structure is higher than rooftop solar mounting structure.
- Availing the space for carport mounting structure is also one of the common challenges.
6. Tracking System Mounting Structure
A solar tracking system is a technology which tracks the sun’s trajectory and orient the solar panels accordingly. It ensures that the solar panel faces the sun at 90-degree angle for the maximum period of a day. As a result, the productivity of a solar system is maximum in this tracking system solar panel structure.
Tracking system mounting structures for solar modules are of 2 types: i. Single axis, ii. Dual axis.
| Types of tracking system mounting structures | |
| Single Axis | Dual-axis |
| Tracks the sun’s movement only in 1 direction: it can be either North-South or East-West. | Tracks the sun’s movement in both North-South and East-West directions |

Advantages of Tracking System Mounting Structure:
- It helps you generate maximum solar electricity over the day.
- Corrects the panel orientation automatically to increase efficiency
Disadvantages Tracking System Mounting Structure:
- Its installation cost is much higher (know about the solar tracker price).
- As the installation process is complex, you need to hire an expert solar engineer to install solar trackers.
- The maintenance of the tracking system solar mounting structure is challenging
Solar Batteries
You may store extra electricity produced by your solar panels by adding a solar battery to your solar power system. The stored energy can be used to power your home during periods such as nights, overcast days, and power outages when your solar panels aren’t producing enough electricity. Helping you use more of the solar energy equipment you’re producing is the goal of a solar battery. Without battery storage, any extra electricity generated by your solar panels is sent to the grid, meaning you are producing power and distributing it to others without fully utilizing the electricity your panels produce first.
Types
1. Lithium-ion batteries
Because of its higher DoD, dependable longevity, greater energy storage capacity, and smaller size, lithium-ion battery technology is preferred by battery makers, as was previously noted. However, lithium-ion batteries are more costly than lead-acid batteries despite their many advantages.
2. Lithium iron phosphate battery
The LiFePO4 battery has the edge over lithium-ion, both in terms of cycle life (it lasts 4-5x longer), and safety. This is a key advantage because lithium-ion batteries can overheat and even catch fire, while LiFePO4 does not.
3. Lead-acid batteries
Long in use as in-home energy storage devices for off-grid power sources, lead-acid batteries share technology with the majority of automobile batteries. Even while they are still reasonably priced, their short lifespan and low DoD are making them less and less popular.
Solar Energy Monitoring Systems
Software (such a web portal or phone app), hardware connected to a solar array, and an internet connection are all components of a solar monitor. The data passing through the inverters of a solar array is read by the monitor. Leading manufacturers SolarEdge and Enphase have integrated solar monitors into their inverters.
Software is the key to solar monitors; it may be used to monitor current system output, identify problems or hardware flaws, and compile historical data to compare panel performance over time. To determine the financial performance of your solar system, you can export the data to financial software. Users can discover where they can improve their energy efficiency by comparing their solar output and energy consumption using software that is integrated with other home energy use programs. To charge an EV at the most economical or efficient time, SolarEdge’s app, for instance, can link a solar array to the business’s internet-connected EV charger.
Solar Charge Controllers
An electronic device called a solar charge controller is used in off-grid and hybrid off-grid applications to control the current and voltage that PV arrays supply to batteries and electrical loads, such as fans, lights, surveillance cameras, communications and process control solar energy equipment, and monitors. Batteries are safely charged by the controller, which also keeps them at a high level of charge without going overboard. While a subpar solar charge controller can result in battery failure and the complete off-grid system shutting down, a high-quality charge controller can prolong battery life. Another name for solar charge controllers is solar charge regulators.
In off-grid systems, solar charge controllers keep batteries at their maximum charge without overcharging them to prevent gassing and battery degradation. This contributes to longer battery life. Additionally, charge controllers provide the right voltage and current to match the rated capacity of electrical loads. The PV array would generate excessive power without a charge controller attached, destroying the loads and batteries.

Types
1. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) charging is a feature of conventional solar regulators that work by connecting the battery bank and solar array directly. The array output voltage is “pulled down” to the battery voltage during bulk charging when the array and battery bank are continuously connected. Depending on the size and properties of the battery as well as the quantity of current supplied by the array, the battery voltage rises a little.
2. Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
The Vmp (maximum power voltage) of the solar array may be swiftly and precisely determined with Morningstar MPPT controllers thanks to TrakStar technology. To identify the voltage at which the array is generating the most electricity, TrakStar MPPT controllers “sweep” the solar input. The controller increases the charging current by harvesting power from the array at this value and converting it to battery voltage.
Conclusion
The transition to renewable energy begins with the right tools, and solar energy equipment is at the forefront of this transformation. From photovoltaic panels and inverters to batteries and monitoring systems, each component plays a vital role in ensuring maximum efficiency, reliability, and sustainability in harnessing solar power.
By investing in high-quality equipment and leveraging advanced technologies, individuals and businesses can reduce their carbon footprint, lower energy costs, and contribute to a greener planet. As solar energy equipment continues to evolve, the equipment powering these systems will become even more efficient, accessible, and essential for meeting global energy demands.
Take the first step toward energy independence today by choosing the right solar energy equipment for your needs—because the future of energy is solar, and the future starts now.