In the world of solar energy, a solar inverter plays a critical role. It is the heart of every solar power system, converting the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC), which can be used to power your home or business. Without the inverter, your solar energy system would be inefficient or practically unusable.
In this detailed guide, we will explore the function, types, benefits, and installation of solar inverters, as well as tips for maximizing their efficiency. Whether you’re looking to install a solar energy system for the first time or upgrade your current system, understanding the role of the solar inverter is key to optimizing your renewable energy investment.
Table of Contents
What is a Solar Inverter?
One tool that transforms solar electricity from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), which is utilized in homes and businesses, is a solar power inverter. Through this conversion, solar energy can be used with appliances and the electrical grid. To ensure that the electricity generated by solar systems may be used to power household appliances and be fed back into the grid, a solar panel inverter is necessary. An apparatus known as a solar power inverter transforms solar-generated DC electricity into AC electricity, which is utilized in residences and commercial buildings. Through this conversion, solar energy can be used with appliances and the electrical grid. Thus, a solar panel inverter makes sure that the power generated by solar panels
Importance of a Solar Inverter
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) is a technique used by solar inverters to optimize solar panel performance. Solar inverters convert DC electricity from solar panels into usable AC electricity for homes, regulate voltage and frequency, manage electricity flow between panels, batteries, and the grid, and ensure system stability. They also enable energy storage and system monitoring. Solar inverters are crucial for maximizing energy production and ensuring safe, efficient solar power systems.
- Energy Conversion: As mentioned, the inverter ensures that the DC energy generated by the solar panels is converted to AC energy, making it usable.
- Performance Monitoring: Many modern inverters come with built-in performance monitoring, allowing users to track their system’s output and ensure that the solar panels are functioning efficiently.
- Safety and Protection: Inverters provide important safety functions, such as shutting down the solar energy system during grid outages, protecting it from overloads, and managing voltage variations.
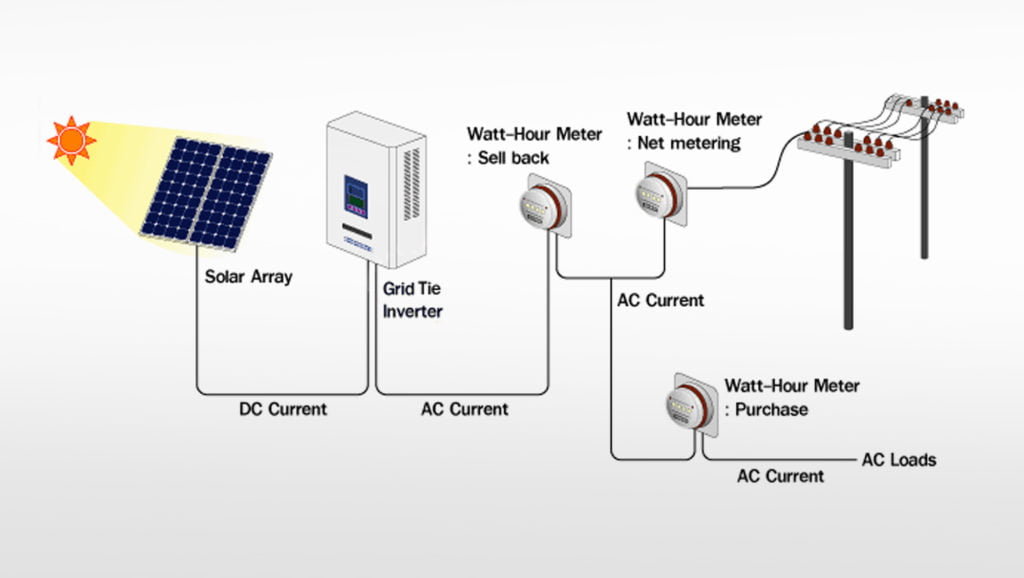
- Grid Connection: If your solar system is connected to the electrical grid, the inverter ensures that the energy you produce meets the grid’s standards for voltage and frequency, allowing for smooth integration and the ability to sell excess energy back to the grid.

Types of Solar Inverters
When choosing a solar inverter, it’s essential to understand the different types available, as each one offers specific advantages depending on the system’s design and your energy needs.
1. String Inverters
String inverters are the last but certainly not the least. The most popular type of inverter for domestic use is a string inverter, which is typically used in single solar installations. The fact that a string of solar panels is attached to them gives them the name “string inverters.”
- Advantages:
- Lower cost
- Simple installation and maintenance
- Centralized control of the solar system
- Disadvantages:
- If one panel in the string is shaded or underperforming, it can affect the performance of the entire string.
- Limited flexibility when adding more panels in the future.

2. Microinverters
Microinverters are small devices attached to each solar panel that convert power independently, allowing each panel to operate at peak performance, regardless of the conditions affecting its neighbors. This means that shading on one panel does not impact the others. They also enable individual panel performance monitoring, helping identify issues early. While microinverters are typically more expensive than string inverters, they can increase overall system efficiency and make it easier to expand power capacity if needed, such as when adding more panels to charge an electric car.
- Advantages:
- Panel-level optimization, meaning each panel operates independently.
- Ideal for roofs with shading issues or complex designs.
- Easier to expand the system by adding panels.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher upfront costs
- More complex installation and maintenance

3. Central Inverter
Central inverters are large devices used in solar power plants to convert the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be fed into the electrical grid.
- Advantages:
- Increased system efficiency compared to string inverters.
- Lower cost than microinverters.
- Ideal for shaded areas and complex roof designs.
- Disadvantages:
- Slightly higher costs than traditional string inverters.
- Requires additional components, increasing installation complexity.

4. Hybrid Inverters
A hybrid solar inverter combines a solar inverter and a battery inverter into one unit, allowing it to manage power from solar panels, batteries, and the utility grid simultaneously. It converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) for home use and can send excess electricity to the grid. The hybrid inverter also manages the conversion of stored DC electricity from batteries into AC. This all-in-one device improves the efficiency of traditional solar inverters by facilitating grid connections, solar charging, and, when necessary, drawing power from the grid to charge battery storage, adapting to variable solar energy availability.

5. Power Optimizer
Power optimizers are a middle ground between string inverters and micro-inverters, both in function and cost. Each solar panel has an optimizer that enhances the DC current before sending it to a central inverter for conversion to AC power. This setup prevents the entire system from being slowed by a single underperforming panel, offering more efficiency than string inverters while being less expensive than micro-inverters. As technology improves, the popularity and affordability of power optimizers are increasing.
- Advantages:
- More efficient than string inverters
- Less expensive than micro-inverters
- Individual panel monitoring available
- Disadvantages:
- Higher initial cost
- Not necessary if all panels face the same way and are not shaded

Facts About Solar Inverters for Solar Energy Systems
1. Solar Inverters Convert DC to AC Power
Solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity, which most homes and businesses can’t use directly. A solar inverter converts this DC into alternating current (AC), the standard for powering appliances and feeding energy into the grid.
2. Types of Solar Inverters
There are three primary types of solar inverters: string inverters, microinverters, power optimizers, hybrid inverters, and central inverters. Each serves different needs depending on your system design, budget, and shading conditions.
3. String Inverters Are the Most Common
String inverters are widely used due to their cost-effectiveness and reliability. However, they are best suited for systems with minimal shading and simple layouts where all panels receive similar sunlight.
4. Microinverters Offer Panel-Level Optimization
Microinverters work independently for each solar panel, ensuring that shading on one panel doesn’t reduce the performance of the entire system. They’re ideal for complex roof designs or areas with inconsistent shading.
5. Power Optimizers Combine the Best of Both Worlds
Power optimizers combine the benefits of string inverters and microinverters. They optimize the output of individual panels but use a centralized string inverter for AC conversion, providing a balance between cost and efficiency.
6. Hybrid Inverters Include Battery Storage
Hybrid inverters are designed to work with solar battery storage systems. They allow you to store excess energy produced during the day for use at night or during grid outages, enhancing energy independence.
7. Efficiency Matters
The efficiency of a solar inverter can directly impact your system’s performance. Most modern inverters have an efficiency rating between 95% and 99%, meaning only a small percentage of the energy is lost during conversion.
8. Inverter Lifespan is Shorter than Solar Panels
While solar panels can last 25 to 30 years, solar inverters typically have a lifespan of 10 to 15 years. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help extend their life, but replacements will likely be needed during the system’s lifetime.
9. Cost Considerations
The cost of solar inverters can vary significantly based on the type and features. As of recent estimates:
- String Inverters: Typically range from $1,000 to $3,000.
- Microinverters: Usually range from $1,500 to $3,500 for a system.
- Hybrid Inverters: Often priced between $2,000 and $5,000, depending on the battery capacity and features.
When budgeting for your solar energy system, it’s important to include the inverter costs, as they can significantly impact the overall investment.
10. Technological Advancements
The solar inverter industry is continuously evolving, with advancements that enhance performance and efficiency. Some emerging trends include:
- Integrated Battery Storage: More inverters are being designed to accommodate battery storage systems, allowing for greater energy independence.
- Smart Inverters: These inverters can communicate with the grid, responding to energy demand signals and enhancing grid stability.
- Increased Efficiency: Inverter technologies are improving, reducing energy losses during conversion and boosting overall system performance.
11. Inverters Play a Role in System Safety
Solar inverters are equipped with safety mechanisms, such as anti-islanding protection, which shuts off the system during a power outage to prevent electricity from flowing back into the grid, protecting utility workers and equipment.

Benefits of Solar Inverters
Installing a high-quality solar inverter can enhance the overall performance of your solar energy system, providing several key benefits:
- Maximizing Solar Energy Utilization
A solar inverter ensures that you are utilizing as much energy from your solar panels as possible. The inverter makes the energy produced by the panels usable for your home, helping you reduce reliance on grid electricity. - Reducing Energy Bills
By converting the DC power generated by the solar panels into AC power, a solar inverter enables you to use the energy in real-time. Any excess energy can either be stored in batteries or exported to the grid, potentially earning you credits through net metering programs. - Supporting the Grid
Solar inverters help maintain a stable grid by ensuring that the electricity generated by solar panels complies with grid standards. Grid-tied systems can also send excess electricity back to the grid, reducing the load during peak times. - Ensuring System Safety
Solar inverters come with built-in safety features that protect both the system and the user. For instance, they shut down the system during an outage, preventing backfeeding and protecting utility workers. - Enabling System Monitoring
Modern solar inverters often come with monitoring systems that allow you to track your solar system’s performance in real time. You can see how much energy you’re generating, how much you’re consuming, and identify any issues that may arise with your panels.
How to Choose the Right Solar Inverter
Choosing the right solar inverter depends on several factors:
System Size and Design
For smaller, simpler systems, string inverters may be sufficient. For larger or more complex systems, such as those with shading issues, microinverters or power optimizers may be a better fit. Users must take into account the available space in their house or place of business when accurately planning a solar system. Because microinverters can be positioned beneath solar panels to save space, they are appropriate for smaller installations.
However, as more microinverters would be required to expand the solar system, they could not be as cost-effective in the future. Though they need more room, string, and hybrid inverters are still the best options for larger residences and commercial buildings since they can process more DC input at one central location. In the end, the size and type of the solar installation are determined by the available installation area, which also directs the selection of the inverter kinds.
Quality Certification
When selecting an inverter for your residence, pay close attention to three primary aspects of quality assurance: grid compatibility, performance, and safety. Averter risks are decreased by tight criteria met by the inverter, which is certified by safety organizations like UL 1741 and IEC 62109. Performance standards like IEC 61683 assist users choose inverters that maximize the output of their solar system by verifying efficiency claims. Compatibility certifications such as IEEE 1547 verify a secure connection to the utility grid for grid-tied inverter systems. The inverter’s quality is further guaranteed by reliability certifications from reputable labs like TÜV Rheinland. Check with the manufacturers for various certifications in these categories to make sure your inverter satisfies high criteria.
Future Expansion Plans
The distinctions between the four types of inverters are important information for anyone using solar power. Among them, hybrid inverters are a good choice for customers who want to install battery storage systems or other future improvements. Many customers would rather use hybrid inverters rather than buy solar batteries at first. Choosing a hybrid inverter in this situation can function as a grid-tied inverter.
The hybrid inverter provides flexibility without adding to the cost of a separate battery inverter, should the user choose to change the current hybrid system into an energy storage system. To power electric loads, most hybrid inverters can smoothly switch from DC to AC, and vice versa to charge solar batteries. Installing a hybrid inverter would therefore be advantageous for customers that intend to grow their inverter system in the future.
After-Sales Service
The manufacturer’s after-sales service should be taken into account by consumers when selecting the best home solar inverter. Reputable companies like Growatt offer prompt support for warranty claims, troubleshooting, and maintenance advice. To reduce system downtime and financial losses, Growatt provides prompt technical support for diagnosing and fixing problems. Customers should confirm that the manufacturer’s website has readable, unambiguous warranty rules and instructions. Furthermore, Growatt offers a thorough maintenance guide with illustrated instructions and a step-by-step procedure to assist corporate and residential owners in performing preventive maintenance on their inverters. With this degree of assistance, customers can maximize the functionality and lifetime of their solar investment with the assurance of continuous technical support.

Safety Features of Solar Inverters
Modern solar inverters come equipped with various safety features to protect both the system and the user. These include:
Overvoltage Protection: Overvoltage protection safeguards the solar inverter from voltage spikes that can occur due to lightning strikes, grid fluctuations, or other electrical disturbances. The inverter detects excessive voltage levels and disconnects from the grid or the solar panels to prevent damage. This feature helps maintain the integrity of the inverter and the entire solar power system.
Ground Fault Protection: Ground faults occur when the electrical current strays from its intended path, which can lead to short circuits and fires. Solar inverters are equipped with ground fault detection systems that monitor the electrical flow. If a ground fault is detected, the inverter automatically shuts down to prevent further damage or hazards.
Arc Fault Detection: Arc faults are unintended electrical discharges that can cause fires, particularly in solar installations where wiring is exposed to environmental factors. Many modern solar inverters include arc fault detection technology that identifies and interrupts arc faults. This feature enhances safety by minimizing the risk of fire associated with electrical arcs.
Automatic Shutdown: Automatic shutdown is a critical safety feature that activates during grid outages or maintenance. When the grid goes down, the inverter automatically disconnects to prevent back feeding electricity into the grid. This ensures the safety of utility workers and protects the inverter from damage.
Overheating Protection: Overheating can severely damage electronic components within a solar inverter. Many solar inverters are designed with built-in temperature sensors that monitor operating temperatures. If the inverter overheats, it can automatically reduce output or shut down to prevent damage.
Compliance with Safety Standards: Solar inverters must comply with various international and local safety standards. Compliance ensures that the inverter meets rigorous safety requirements, reducing the risk of electrical hazards. Look for inverters certified by reputable organizations, such as Underwriters Laboratories (UL) or the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
Installation of Solar Inverters
A solar inverter is typically installed by a professional solar installer. Here’s a general overview of the installation process:
- Site Assessment: Before installation, the installer will assess your property and determine the best location for the inverter. In most cases, inverters are installed near the main electrical panel for easy access.
- Inverter Mounting: The inverter is mounted on a wall or installed inside a weatherproof enclosure to protect it from the elements.
- Electrical Connections: The inverter is connected to the solar panels and the electrical grid, ensuring the energy generated by the panels can be converted and distributed properly.
- Testing and Commissioning: After installation, the system is tested to ensure it is functioning correctly. The installer will also provide instructions on how to monitor the system’s performance.
Maintenance Tips for Solar Inverters
To ensure that your solar inverter functions optimally and has a long lifespan, regular maintenance is essential. Here are a few tips to help maintain your solar inverter:
- Regular Cleaning: Dust and debris can accumulate on the inverter’s vents, causing it to overheat. Ensure the area around the inverter is clean and well-ventilated.
- Monitor Performance: Use the inverter’s monitoring system to keep an eye on performance metrics. If there’s a sudden drop in energy production, it could indicate an issue with the inverter.
- Inspect for Damage: Regularly inspect the inverter for signs of wear or damage, such as cracks or loose wires. If you notice any issues, contact your installer for repairs.
- Check for Firmware Updates: Many modern inverters come with software that requires periodic updates to ensure optimal performance. Check with the manufacturer for firmware updates.
Future Trends in Solar Inverters
As the demand for solar energy grows, solar inverter technology is also advancing. Some emerging trends include:
- Smart Inverters: These inverters are equipped with advanced grid support features, allowing them to respond to grid signals and support grid stability during outages or voltage fluctuations.
- Increased Efficiency: Inverters are becoming more efficient, reducing energy loss during the conversion process and increasing the overall performance of solar systems.
- Integrated Storage Solutions: The integration of energy storage into inverters is becoming more common, allowing homeowners and businesses to store excess energy for later use.
Conclusion
The solar inverter is a crucial component of any solar energy system, responsible for converting DC energy into usable AC energy. Understanding the different types of inverters and their functions will help you make informed decisions when designing or upgrading your solar energy system. By choosing the right inverter, performing regular maintenance, and staying informed about the latest technological advancements, you can ensure your solar energy system operates efficiently for years to come.
For businesses and homeowners looking to embrace clean energy, investing in a high-quality solar inverter is essential for maximizing your system’s performance and return on investment.
Find Your Perfect Solar Inverter! Ready to choose the right solar inverter for your system? Schedule a consultation with our experts to explore your options and maximize your energy efficiency!
